Sun Sensor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
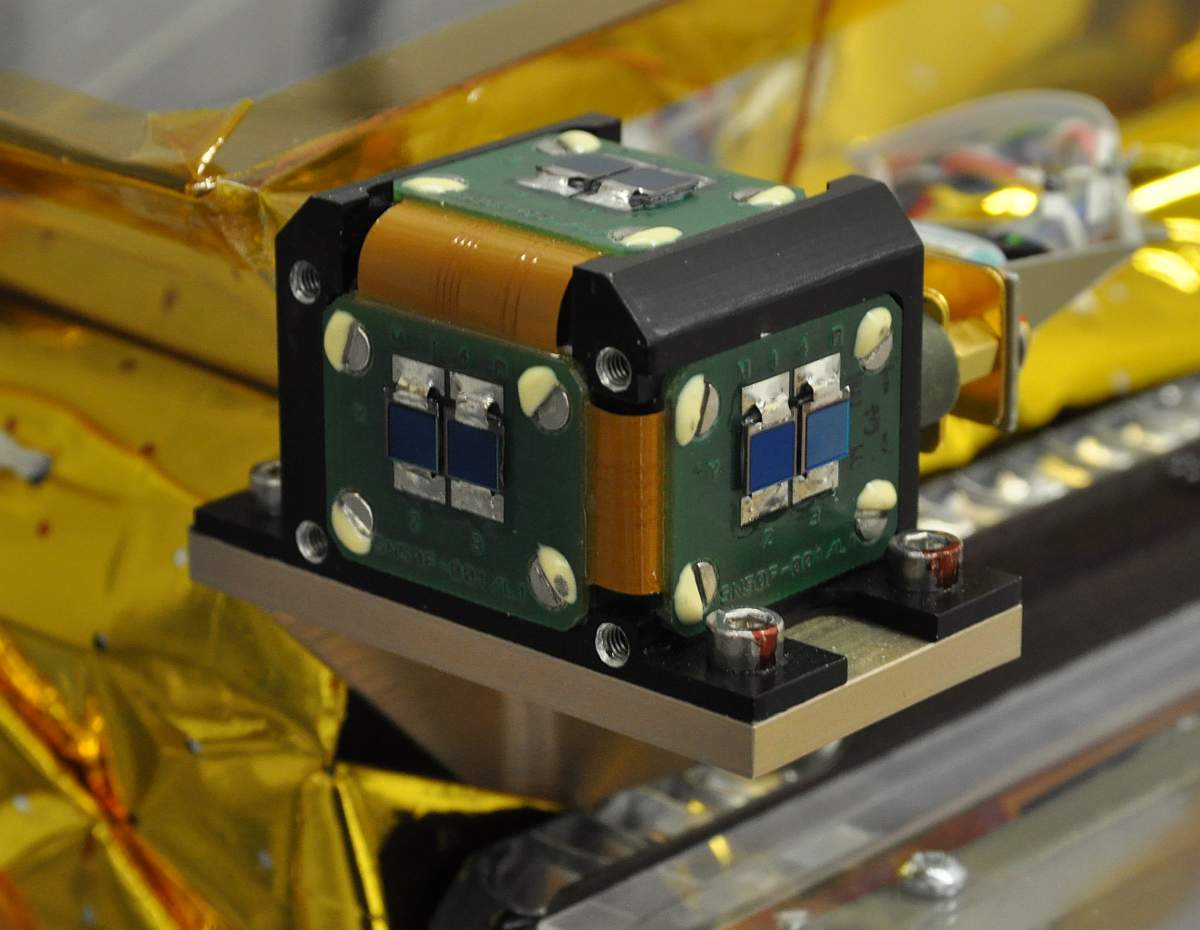 A sun sensor is a
A sun sensor is a
 A sun sensor is a
A sun sensor is a navigational instrument Navigational instruments are instruments used by nautical navigators and pilots as tools of their trade. The purpose of navigation is to ascertain the present position and to determine the speed, direction, etc. to arrive at the port or point o ...
used by spacecraft
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, Earth observation, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, p ...
to detect the position of the sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
. Sun sensors are used for attitude control
Attitude control is the process of controlling the orientation of an aerospace vehicle with respect to an inertial frame of reference or another entity such as the celestial sphere, certain fields, and nearby objects, etc.
Controlling vehicle ...
, solar array
A photovoltaic system, also PV system or solar power system, is an electric power system designed to supply usable solar power by means of photovoltaics. It consists of an arrangement of several components, including solar panels to absorb and ...
pointing, gyro
Gyro may refer to:
Science and technology
* GYRO, a computer program for tokamak plasma simulation
* Gyro Motor Company, an American aircraft engine manufacturer
* ''Gyrodactylus salaris'', a parasite in salmon
* Gyroscope, an orientation-sta ...
updating, and fail-safe
In engineering, a fail-safe is a design feature or practice that in the event of a specific type of failure, inherently responds in a way that will cause minimal or no harm to other equipment, to the environment or to people. Unlike inherent safe ...
recovery.
In addition to spacecraft, sun sensors find use in ground-based weather stations and sun-tracking systems, and aerial vehicles including Balloon (aeronautics), balloons and Unmanned aerial vehicle, UAVs.
Mechanism
There are various types of sun sensors, which differ in their technology and performance characteristics. Sun presence sensors provide a binary number, binary output, indicating when the sun is within the sensor's field of view. Analog electronics, Analog and digital electronics, digital sun sensors, in contrast, indicate the angle of the sun by continuous and discrete signal outputs, respectively. In typical sun sensors, a thin slit at the top of a rectangular chamber allows a line of light to fall on an array of photodetector cells at the bottom of the chamber. A voltage is induced in these cells, which is registered electronically. By orienting two sensors perpendicular to each other, the direction of the sun can be fully determined. Often, multiple sensors will share processing electronics.Criteria
There are a number of design and performance criteria which dictate the selection of a sun sensor model: *Field of view *Angular resolution *Accuracy and precision, Accuracy and Stochastic drift, stability *Mass and volume *Input voltage and power *Output characteristics (including electrical characteristics, update frequency, nonlinearity, and encoding) *Durability (including radiation hardening and tolerance to vibration and residual stress, thermal cycling)See also
* Celestial navigation * Earth sensor * Star trackerReferences
{{Reflist, refs= {{cite web, title=Digital Sun Sensors (DSS), url=http://www.adcole.com/aerospace/digital-sun-sensors/, publisher=Adcole Corporation, accessdate=11 March 2016 {{cite web, title=High Accuracy Fine Sun Sensors, url=http://www.adcole.com/aerospace/high-accuracy-fine-sun-sensors/, publisher=Adcole Corporation, accessdate=11 March 2016 {{cite web, title=LIASS: LInear Accurate Sun Sensor, url=http://www.space-airbusds.com/media/document/gnc_1_liass_2015-v_std_b-def.pdf, publisher=Airbus Defense & Space, accessdate=11 March 2016 {{cite web, title=What is a Sun Sensor?, date = 17 June 2013, url=http://www.azosensors.com/Article.aspx?ArticleID=223, publisher=AZO Sensors, accessdate=11 March 2016 Spacecraft attitude control Astrodynamics Orbits Spaceflight concepts Navigational equipment Celestial navigation